Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
Isomerism in Coordination Compounds: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Isomerism in Coordination Compounds, Structural Isomerism, Ionization Isomerism, Hydrate Isomerism, Coordination Isomerism, Linkage Isomerism, Polymerisation Isomerism, etc.
Important Questions on Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
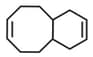
Number of geometrical isomer of given compound will be:
Among the following, a pair of resolvable configurational enantiomers is given by:
How many minimum no. of C-atoms are required for position and geometrical isomerism in alkene?
Which of the following compounds does exhibit stereoisomerism?
Which of the following has largest number of isomers?
(R is alkyl group, en is ethylediamine).
How to calculate theoretically geometrical isomers in type octahedral complex.
The possible geometrical isomers of octahedral complex are
The possible geometrical isomers of the octahedral complex are fifteen.
The complexes : and are the example of which type of isomerism ?
The possible geometrical isomers of octahedral complex are _____.
The number of enantiomers possible for Octahedral Complex is two.
The number of Stereoisomers possible for Octahedral Complex is four.
The number of enantiomers possible for Octahedral Complex is _____.
The number of Stereoisomers possible for Octahedral Complex is _____.
The number of geometrical isomers possible for Octahedral Complex is .
The number of Stereoisomers possible for Octahedral Complex is .
The number of geometrical isomers possible for Octahedral Complex is _____.
The number of Stereoisomers possible for Octahedral Complex is _____.
The number of Geometrical isomers possible for Octahedral Complex is zero.
The number of Stereoisomers possible for Octahedral Complex is three.
